《1,3,5-Trifluorobenzene endorsed EC-free electrolyte for high-voltage and wide-temperature lithium-ion batteries》
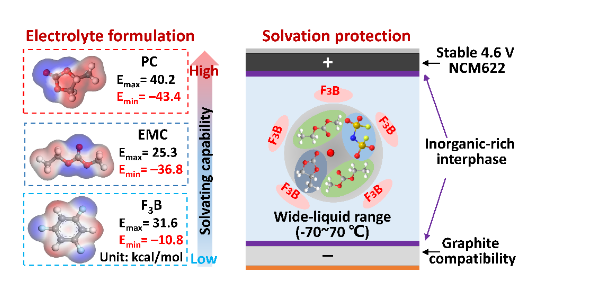
Ethylene carbonate (EC) is prone to interfacial side reactions on the surface of high-nickel cathode, and its application in high-voltage lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) is limited. Removing EC from the electrolyte can obtain good oxidation stability, but it will cause the interface deterioration of the electrode material and the decomposition of the electrolyte. In this work, an EC-free lithium-ion battery electrolyte based on a gradient solvation structure was developed by introducing a functional co-solvent (1,3,5-trifluorobenzene, F3B) into an electrolyte system of propylene carbonate (PC)/methyl ethyl carbonate (EMC). F3B does not participate in solvation shells, but preferentially decomposes at the interface to build a robust interfacial phase and inhibits solvent decomposition and electrode corrosion. The electrolyte exhibits good interfacial compatibility, high voltage stability (LiNi0.6Mn0.2Co0.2O2, NCM622 cut-off voltage 4.6 V) and wide liquid domain (-70~77 °C) at conventional lithium salt concentration (1.1 M). The NCM/graphite pouch battery based on this electrolyte still retains 81.1% capacity after 600 cycles at 0.5C. This work opens up new avenues for the development of high-voltage electrolytes for next-generation lithium-ion batteries.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2095495623003480
