《Multidentate Ether Modifies Solvation Structure in Nonflammable Phosphate Electrolytes for Wide-Temperature Lithium-ion Batteries》
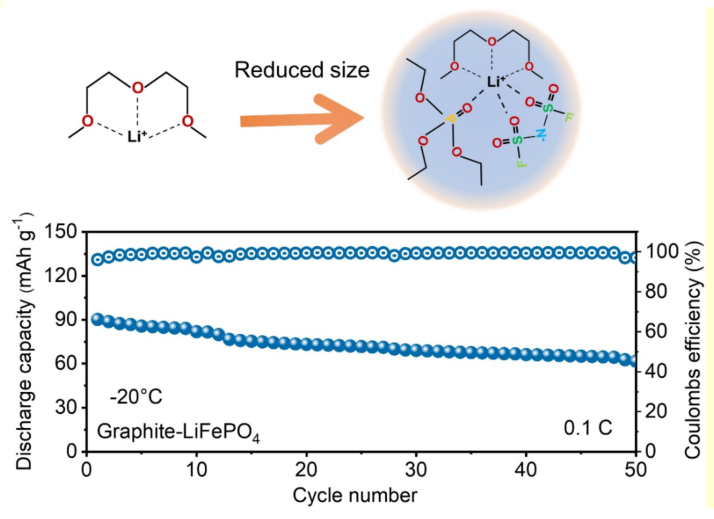
Conventional carbonate electrolytes cannot meet the requirements for lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) with wide temperature range and high safety.Diethyl ethylphosphonate (DEEP) has excellent flame retardancy and a wide temperature range (-83 to 198 °C), which holds promise for developing a non-flammable electrolyte for wide-temperature application inLIBs. However, its limited compatibility with graphite electrodes and slow ionic transport capability must be addressed. Herein, we introduce diethylene glycol dimethyl ether (DEGDME) to reconfigure the solvation structure of DEEP-based electrolyte and enhance its ion transport capacity. The film-forming additives enable the electrolyte to preserve 98%capacityretentionafter 150 cyclesforLi||Graphite cells. The non-flammable DEEP-based electrolytes modified with DEGDMEenableimproved low-temperature performancewith achieving71%50th-cycle retention ofGraphite||LiFePO4cells at-20°C.This work introduces a new strategy for designing non-flammable phosphate electrolytes, enabling the reliable and safe application ofLIBsacross a wide temperature range.