《Origin of the high conductivity of the LiI-Doped Li3PS4 electrolytes for all-solid-state Lithium-sulfur batteries working in wide temperature ranges》
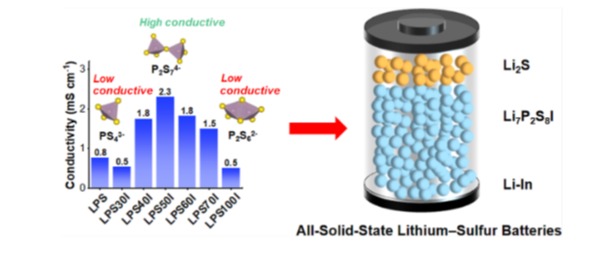
Sulfide electrolytes with high ionic conductivity and low interfacial resistance have great application potential in all-solid-state batteries. The structure of the P-S backbone in the sulfide electrolyte composition plays a crucial role in conductivity. The introduction of lithium iodide into the Li3PS4 structure can modify the P-S backbone to achieve high ionic conductivity. In this paper, the doping rate of lithium iodide was optimized by ball milling and sintering process, and the phase transition and structural evolution of the P-S skeleton in Li3PS4-50% lithium iodide electrolyte (also known as Li7P2S8I) and 50% composition were obtained. The preparation of all-solid-state lithium-sulfur batteries was prepared by using Li7P2S8I electrolyte combined with nano-Li2s cathode and lithium anode, which can achieve an initial discharge capacity of 739.7 mAh g-1 and a cycle capacity retention rate of 70.0%. When the operating temperature rises to 60 oC, its discharge capacity reaches 862.8 mAh g-1, and the capacity decays rapidly. However, when 70 cycles above 0°C, it shows stable performance and good cycling performance. The results of EIS and in-situ pressure show that the difference in electrochemical performance of assembled batteries at different operating temperatures is related to the interfacial resistance caused by volume change. This study provides a strategy for the preparation of highly conductive sulfide electrolytes for solid-state batteries, and reveals the influence of temperature on the electrochemical performance of all-solid-state lithium-sulfur batteries.
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.iecr.2c04158
